Feedback control systems are the unsung heroes of modern technology, seamlessly orchestrating operations across a myriad of applications. From regulating temperature in your home to optimizing performance in industrial processes, these systems play a crucial role in ensuring efficiency, stability, and precision.
Understanding Feedback Control Systems
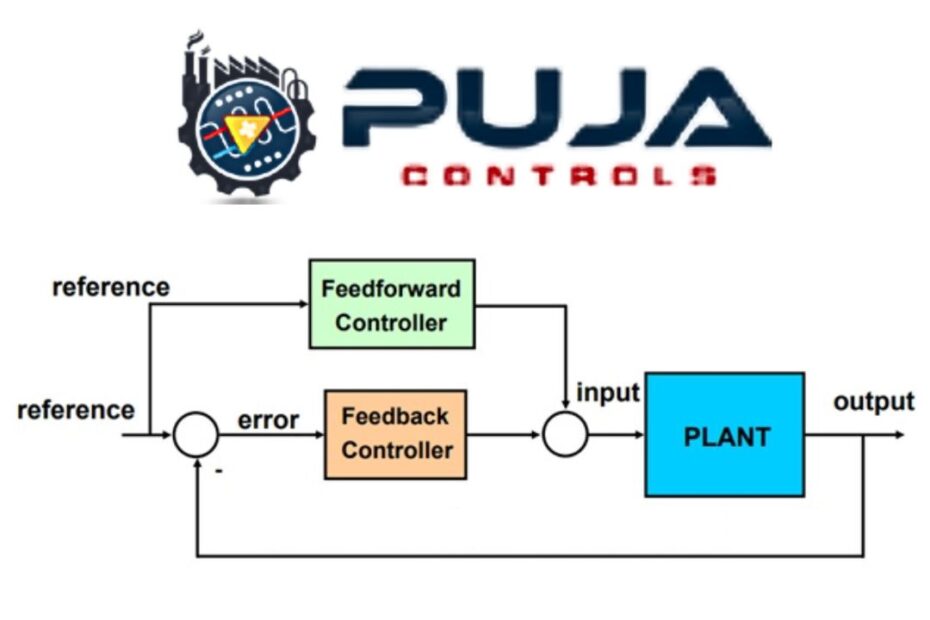
Feedback control systems utilize sensors to measure the output or performance of a system. Further they compare it to a desired reference or setpoint, and then make adjustments to the system’s inputs to bring the output closer to the desired value. This continuous loop of sensing, comparing, and adjusting forms the backbone of feedback control systems.
Applications of Feedback Control Systems in Everyday Life
- Home Thermostats: In your home, control systems are at work in thermostats, ensuring that your living space stays at your desired temperature by regulating heating and cooling systems.
- Automobile Cruise Control: Cruise control in vehicles utilizes feedback control to maintain a constant speed set by the driver, adjusting throttle input as needed to counteract changes in terrain or wind resistance.
- Audio Systems: They are also present in audio equipment, maintaining sound quality by adjusting volume levels to compensate for changes in input signal strength.
Industrial and Commercial Applications
- Manufacturing Processes: In manufacturing, feedback control regulate various parameters such as temperature, pressure, and flow rates to ensure consistent product quality and production efficiency.
- Chemical Processing: They are essential in chemical processing plants, where precise control of reactions and ingredient ratios is critical for safety and product quality.
- Power Generation: Power plants utilize control systems to maintain grid stability, adjust power output in response to demand fluctuations, and prevent equipment damage.
Applications Across Industries
Feedback control systems find applications in a wide range of industries, each with its unique set of challenges and requirements:
- Manufacturing: In manufacturing, they regulate processes such as robotic assembly, CNC machining, and quality control. Hence ensuring consistent product quality and high throughput.
- Energy: In the energy sector, they optimize power generation and distribution, manage grid stability, and enhance renewable energy integration.
- Healthcare: In healthcare, these systems control medical devices and equipment, monitor patient vital signs, and assist in surgical procedures, improving patient outcomes and safety.
- Aerospace: In aerospace, control systems govern aircraft flight controls, navigation systems, and propulsion. Thus ensuring safe and efficient operation in the skies.
Advantages of Feedback Control Systems
- Accuracy: They excel at providing precise control over system parameters, ensuring that outputs closely match desired setpoints.
- Robustness: These systems are capable of adapting to changes in operating conditions, making them resilient to disturbances and external factors.
- Efficiency: By continuously monitoring and adjusting system inputs, control systems optimize performance and resource utilization, leading to increased efficiency.
Challenges and Limitations
- Complexity: Designing and implementing feedback control systems can be complex. Therefore requiring careful consideration of system dynamics, sensor accuracy, and control algorithms.
- Tuning: Proper tuning of feedback control systems is essential for optimal performance, often requiring expertise and iterative adjustment.
- Nonlinearity: Some systems exhibit nonlinear behavior, posing challenges for feedback control algorithms designed for linear systems.
Future Trends and Innovations
- Smart Grids: The integration of control systems into power distribution networks enables the creation of smart grids. These are capable of dynamically adjusting energy flow and optimizing resource utilization.
- Machine Learning: Advancements in machine learning algorithms offer new opportunities for enhancing feedback control systems. Further allowing for adaptive tuning and predictive maintenance.
- Internet of Things (IoT): The proliferation of IoT devices enables the collection of real-time data from a multitude of sources. Therefore it provides valuable insights for feedback control to improve performance and efficiency. Also read how IoT is useful in agriculture.
Conclusion
In conclusion, they are indispensable components of modern technology, driving efficiency, stability, and precision across a wide range of applications. These systems quietly work behind the scenes, ensuring smooth operations and enhancing our quality of life. As technology continues to evolve, control systems will play an increasingly vital role in shaping the future of automation, sustainability, and innovation.